What is a Marine Radar?
Marine radar stands as a pivotal technology in the realm of maritime navigation and safety. This detailed exploration aims to unpack the essentials of marine radar, from its fundamental definition to its historical development, underscored by its crucial role in ensuring safe and efficient marine operations.Defining Marine Radar
Marine radar operates as a critical navigational aid used extensively in the maritime world. It is a detection system that:- Utilizes radio waves to identify objects, landmasses, and other vessels in its vicinity.
- Measures the distance and bearing of these objects from the vessel to help in navigation and avoidance maneuvers.
The Evolution of Marine Radar
The history and development of marine radar encompass several key milestones:- Origins in Military Applications: Initially developed for military use during World War II, radar technology has been adapted for marine navigation.
- Post-War Expansion: Following the war, the peacetime application of radar technology expanded into the maritime industry, revolutionizing navigation and safety at sea.
- Technological Advancements: Over the years, marine radar has evolved significantly, incorporating digital processing and enhanced detection capabilities to meet modern maritime safety standards.
- Key Point: This evolution underscores a trajectory of improvement and adaptation, underscoring radar's integral role in maritime history.
The Importance of Marine Radar in Maritime Navigation and Safety
Marine radar is not just about technology; it's an essential tool for safety and navigation:- Collision Avoidance: It serves as a primary means for avoiding collisions in busy sea lanes or poor visibility conditions.
- Navigation Aid: Radar aids in navigation close to shorelines or in the open sea by identifying landmarks and navigation markers.
- All-Weather Operation: Capable of operating in all weather conditions, ship radars ensure continuous safety.
Contributions to Effective and Safe Marine Operations
The role of marine radar extends beyond mere detection, influencing broader aspects of marine operations:- Situational Awareness: Provides real-time images and data on immediate surroundings, enhancing situational awareness.
- Global Positioning Integration: When integrated with global positioning systems (GPS), marine radar offers comprehensive navigational efficiency.
- Safety Enhancement: By allowing early detection of potential hazards, marine radar plays a critical role in reducing the risk of maritime accidents.
- Key Point: Marine radar's contributions to maritime operations are multifaceted, spanning safety, operational efficiency, and navigational accuracy.

How Does Marine Radar Work?
The sophistication of marine radar emerges from its intricate technology and distinctive advantages over other navigational aids like GPS. Delving into its operational specifics offers fascinating insights into the safety and efficiency shipboard radar brings to the maritime world.Technical Operation of Marine Radar
Marine radar operates on the principles of radio wave emissions to navigate and identify potential hazards in the marine environment. The following bullet points break down its operational process:- Radio Wave Transmission: Marine radar systems emit a pulse of radio waves from a rotating antenna mounted on the vessel.
- Reflection and Detection: These waves, once they hit an object, are reflected back to the radar unit, where the system detects them.
- Data Analysis: The radar's processor interprets this reflected signal to ascertain the distance, size, and movement of the object in relation to the vessel.
- Display Output: The processed data is then depicted on the radar screen, allowing the navigator to visualize the maritime scenario surrounding the ship.
Marine Radar Versus GPS Technology
While GPS technology is integral to modern navigation, marine radar offers specific advantages that are paramount in certain maritime situations:- Operational Independency: Unlike GPS, which relies on satellite signals, marine radar operates independently, unaffected by satellite availability or signal interference.
- Immediate Environment Mapping: Marine radar provides detailed imagery of the immediate surroundings, not just positional data. It gives navigators a visual understanding of what's around them, something GPS cannot replicate.
- All-Weather Performance: GPS signals can be degraded during harsh weather conditions, while marine radar is designed to perform reliably regardless of weather, presenting vital navigational data even in poor visibility.
- Collision Avoidance: Most importantly, marine radar excels in collision avoidance with real-time tracking of multiple targets, offering a level of situational awareness in crowded or obstructed waters that GPS lacks.

Advanced Features of Marine Radar
Marine radar technology has evolved far beyond mere object detection, incorporating a suite of advanced features that enhance navigational accuracy, safety, and situational awareness for mariners.- Doppler Target Tracking: This feature leverages the Doppler effect to distinguish moving targets from stationary ones, making it easier for navigators to identify potential threats. It significantly enhances collision avoidance by providing clear indications of moving objects in the vessel's vicinity.
- RangeFusion Technology: RangeFusion technology combines data from different radar ranges into one cohesive picture. It allows for seamless viewing of far and near targets simultaneously, offering a comprehensive overview of the surroundings that enhances decision-making accuracy.
- Radar Overlay on Chart: Integrating marine radar data directly onto digital navigation charts ensures a more intuitive understanding of the surroundings. This overlay provides a visual representation of radar targets over navigational charts, merging two crucial data sources for superior navigational awareness.
- Target True Trails Display: This feature enhances the ability to gauge the movement direction and speed of other vessels. By displaying the true trails of targets, mariners can predict their future positions, enabling more informed decision-making processes for collision avoidance.
- AIS Integration: The Automatic Identification System (AIS) integration combines radar and AIS data, offering a comprehensive view of vessel identities, positions, and movements. This synergy facilitates a deeper understanding of traffic scenarios, particularly in congested waterways.
- Stabilized PPI Display: The Plan Position Indicator (PPI) is stabilized against the vessel’s own motion, ensuring that the radar image remains consistent and clear, regardless of sea conditions. This stability is crucial for the accurate interpretation of the radar data.
- MARPA Target Tracking: The Mini Automatic Radar Plotting Aid (MARPA) function allows the user to manually track specific targets, providing detailed information on their course, speed, and closest point of approach. This feature is instrumental in high-traffic situations, offering a detailed assessment of potential collision threats.

Choosing the Right Marine Radar for Sale
When it comes time to select the best marine radar for your vessel, pondering over the vast range of options can be daunting. Nonetheless, honing in on a few key factors will lead you to the marine radar that best meets your seafaring needs.Factors to Consider for Marine Radar Selection
As we navigate through the choices, it's pivotal to assess specific criteria that will ascertain the alignment of the marine radar with your nautical requirements.Compatibility with Electronics
Central to integrating radar marine into your vessel's navigational suite is ensuring compatibility with existing onboard electronics. This entails:- Connectivity: Check for compatibility with network protocols used by your current devices (e.g., NMEA 2000).
- Integration: Evaluate how the radar will interface with other electronics like multifunction displays (MFDs).
Type of Boat
The style and purpose of your vessel play a determining role:- Size and Hull Material: Larger vessels or those with metal hulls may require more powerful radar systems.
- Usage: Fishing boats may benefit from radars with advanced fish-finding features, whereas yachts might focus more on collision avoidance and chart overlay functions.
Visualization Range Needs
Assessing how far and wide you need your radar to see is crucial:- Short-to-Medium Range: Smaller boats operating near coastlines may only require short to medium-range capabilities.
- Long Range: Ocean-crossing vessels will necessitate radars that can provide a much longer range for early hazard detection.
Power Output
The strength of the radar's signal affects its performance:- Low-Power Radar: Ideal for small boats and close-range detection.
- High-Power Radar: Necessary for bigger vessels or those requiring long-range detection and clear images.
Radar Technology Options
Exploring the type of marine radar technology that meets your navigation style is essential:- Broadband Radar: Offers excellent short-range resolution and minimal radiation, suitable for small to medium boats.
- Magnetron Radar: Traditional radar with longer range and higher power output, fitting for larger vessels.

Marine Radar Applications
Marine radar is an indispensable tool in modern maritime operations. Its scope extends beyond mere object detection, playing a crucial role in various practical applications that ensure the safety and efficiency of navigation at sea.Practical Applications of Marine Radar
Delving into the extensive utility of marine radar, we uncover its significance across different scenarios that mariners commonly encounter.Collision Avoidance
One of the primary uses of marine radar is to prevent collisions. By providing real-time data on the position, speed, and course of nearby vessels, marine radar enables navigators to make informed decisions to avoid potential collisions. This is especially crucial in busy shipping lanes and in adverse weather conditions, where visual observations are limited.Navigation in Poor Visibility
Marine radar proves invaluable in scenarios of poor visibility, such as fog, heavy rain, or at night. It allows mariners to detect landmasses, navigational hazards, and other vessels in their vicinity, ensuring safe passage even when visual cues are absent. This capability is essential for maintaining course accuracy and avoiding natural and man-made obstacles.Weather Formation Tracking
Advanced marine radar systems are capable of detecting weather formations, including storms and squalls, at a considerable distance. This enables the crew to either prepare for incoming bad weather or alter their course to avoid severe conditions. Tracking weather formations contributes significantly to the safety and comfort of those aboard.Safe Navigation through Crowded Harbors
Navigating through crowded harbors and marinas can be challenging, especially for larger vessels. Marine radar assists in these scenarios by providing a clear view of other boats, docks, and obstructions, helping to guide the vessel safely to its berth. This application of marine radar is vital for preventing accidents and ensuring smooth operations in densely populated maritime areas. Through these applications, marine radar establishes itself as an essential component of maritime safety and navigation. Its ability to provide accurate and timely information makes it an invaluable asset for vessels of all sizes, enhancing their operational capabilities and ensuring the safety of the crew and passengers aboard.
Innovations in Marine Radar Technology
The forefront of marine radar technology innovations includes Solid-State X-Band Radar Technology and Pulse Compression Radar. These state-of-the-art upgrades have redefined expectations and capabilities within the maritime industry.Latest Advancements in Marine Radar Technology
Solid-State X-Band Radar Technology
Solid-state X-Band Radar technology represents a significant leap forward in marine radar capabilities. Unlike traditional magnetron radars, solid-state radars use semiconductor devices to generate microwave signals. This transition offers numerous benefits:- Enhanced Reliability: With fewer moving parts and no need for a magnetron (which typically requires regular replacement), solid-state radars are more reliable and have a longer operational life.
- Improved Detection: This technology allows for better detection of small and fast-moving targets, even in high-clutter environments. It ensures enhanced safety for vessels navigating through congested waters.
- Energy Efficiency: Solid-state radars consume less power, making them more energy-efficient and ideal for vessels looking to reduce their environmental footprint.
Pulse Compression Radar
Pulse Compression Radar technology is another groundbreaking advancement that has significantly improved the performance of marine radar systems. It combines the advantages of both high pulse and continuous wave radars, offering:- Superior Resolution and Range: By modulating the radar pulse, pulse compression radar achieves a much higher resolution and range, allowing vessels to detect objects at greater distances and with enhanced clarity.
- Improved Target Separation: This technology enables the radar to separate targets that are close together more effectively, providing a clearer picture of the surrounding waters and increasing navigational safety.
- Reduced Interference: Pulse compression radars are less susceptible to interference from external sources, ensuring more accurate and reliable readings.
Enhancing Safety, Energy Efficiency, and Performance
The innovations in marine radar technology are not just about adopting new techniques; they are about fundamentally improving the way vessels navigate and operate. The transition to solid-state technology and the adoption of pulse compression radar have marked a new era in maritime safety, with systems that are more reliable, efficient, and capable.- Safety: By providing clearer, more accurate radar images and better detecting potential hazards, these technologies significantly enhance maritime safety. They allow for timely decision-making and preventive actions to avoid collisions and navigate safely through adverse conditions.
- Energy Efficiency: The shift towards more energy-efficient radar systems contributes to the maritime industry's ongoing efforts to reduce energy consumption and minimize its environmental impact. These advancements align with global sustainability goals and regulations.
- Performance: The overall performance improvements brought about by these innovations help vessels navigate more confidently and efficiently. With better detection capabilities, enhanced target resolution, and reduced interference, mariners can make more informed decisions, enhancing the safety and efficiency of maritime operations.
World of Marine Radar Software and Apps
In this era of digital transformation, marine radar technology is not confined to standalone hardware units on ships. Numerous software and apps are now available that bring the capabilities of marine radar to smaller vessels, mobile devices, and personal computers. These digital tools complement high-end physical marine radar systems, making advanced maritime navigation features accessible to a wider range of seafarers.Overview of Marine Radar Software and Apps
Marine radar software and apps like Marine Radar Live and Marine Radar App enhance accessibility to radar capabilities and extend the operational possibilities of marine radar systems. This new wave of digital tools targets both professional seafarers and recreational boaters, promoting safety, efficiency, and convenience in maritime navigation.Marine Radar Live and Marine Radar App
Marine Radar Live and Marine Radar App are popular examples of apps that bring marine radar technology to mobile platforms. Leveraging AIS (Automatic Identification System) data, these apps provide real-time tracking of ships around the world. Features typically include:- Live Tracking: Display the real-time location, course, and speed of ships.
- Detailed Information: Provide details about individual vessels, such as dimensions, destination, estimated arrival time, and more.
- Search Function: Allow users to search for specific ships or navigate through different regions.
Marine Radar Systems for Mobile and Other Platforms
Beyond single-purpose apps, comprehensive marine radar systems are also available for mobile and other platforms. Some marine electronics manufacturers have developed apps and software that integrate with their hardware marine radar systems, delivering a cohesive and interactive user experience. Key benefits include:- Remote Access: Enabling users to access and control their onboard radar systems from a handheld device or PC.
- Integrated Data: Presenting radar data alongside chartplotter, sonar, and AIS information for a complete navigational picture.
- Customizable Displays: Allowing users to tailor their display based on individual preferences or specific navigation needs.
Complementing Physical Radar Systems and Enhancing Marine Navigation
Marine radar software and apps are not intended to replace physical radar systems on vessels but to complement them. These digital tools provide increased flexibility, boost situational awareness, and enhance decision-making capabilities, contributing to safe and efficient marine navigation.- Increased Access and Flexibility: Marine radar software and apps extend radar capabilities to devices that crew members and boaters carry with them, providing unprecedented access and flexibility in monitoring vessel movements and maritime conditions.
- Enhanced Situational Awareness: The integration of various data sources within marine radar apps creates a holistic picture of the maritime environment, boosting situational awareness. This comprehensive view aids decision-making and improves navigation safety.
- Support for Cruising and Fishing: For recreational boaters, the combination of radar information with chartplotter and sonar data supports cruising and fishing activities. It allows users to find desirable locations more easily, confirm their position, and avoid potential hazards.
Installing Marine Radar
Marine radar systems are indispensable tools for seafarers, providing essential information to facilitate safe and efficient navigation. Installing a marine radar system on a vessel requires careful planning, correct tools, and a detailed understanding of the boat's construction.General Guidance on Installing Marine Radar Systems on Different Types of Boats
Marine radar installation demands a tailored approach depending on the type and size of your boat. However, there are common factors you should consider during the installation process.Choosing the Right Location
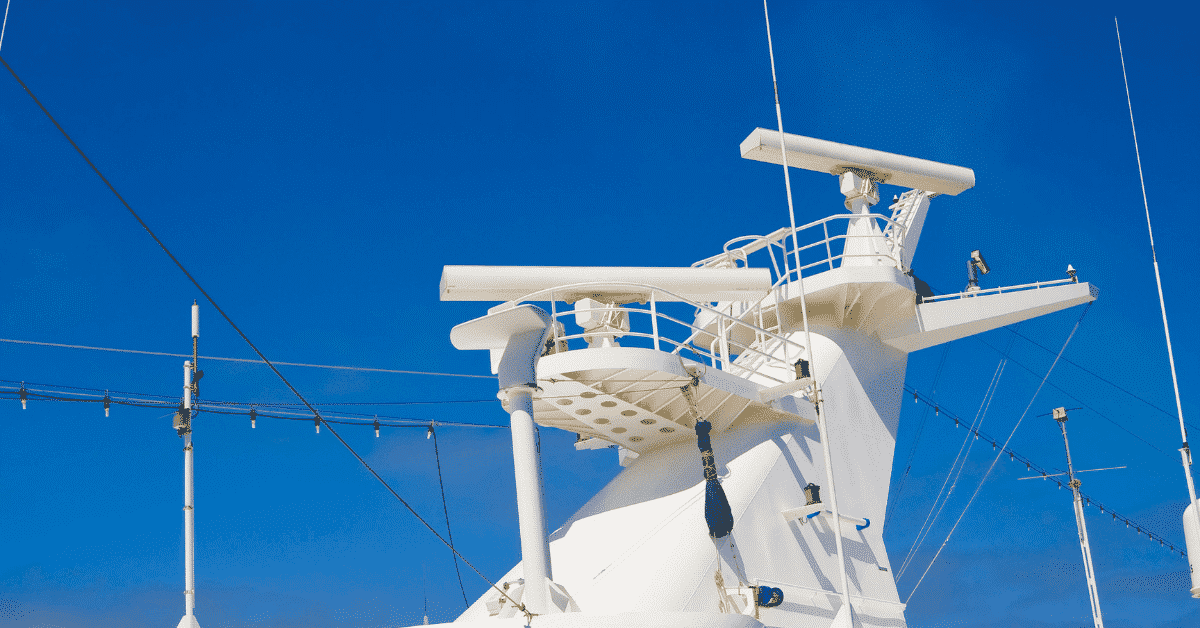
Selecting the right location for your marine radar system is crucial. The radar should be installed at a high point on the boat where it can rotate 360° without any obstruction for optimal performance. For small boats, the radar might be positioned on a radar arch or T-top. Larger vessels might have dedicated masts or radar platforms.Mounting the Radar Unit
Your marine radar system consists of two main parts: the scanner (the rotating part that emits and receives signals) and the display unit. The scanner should be mounted securely at the chosen location, using a radar mount designed for marine environments. Installation instructions provided by the manufacturer should be strictly followed.Running Power and Data Cables
After securing the radar unit, you will need to run power and data cables from the scanner to the display unit. They should ideally be run along existing cable runs and secured with cable ties to prevent movement or damage.Installing the Display Unit
The display unit should be installed at the helm, where it's easily accessible and visible. Make sure there is enough space for the unit and that its location will not interfere with the operation of the boat. connect the cables to the power supply and the unit and it's ready for use.Calibrating the Marine Radar System
Once all hardware parts are installed, you need to follow the instructions in your marine radar system's manual to calibrate the system. This may include setting the range rings, tuning the gain and clutter controls, and familiarizing yourself with various features and methods of operation. Remember to consult a professional installer if you are unsure about any part of the installation process. Ensuring your marine radar system is correctly installed is a crucial step in ensuring your safety at sea.>>Click here view more