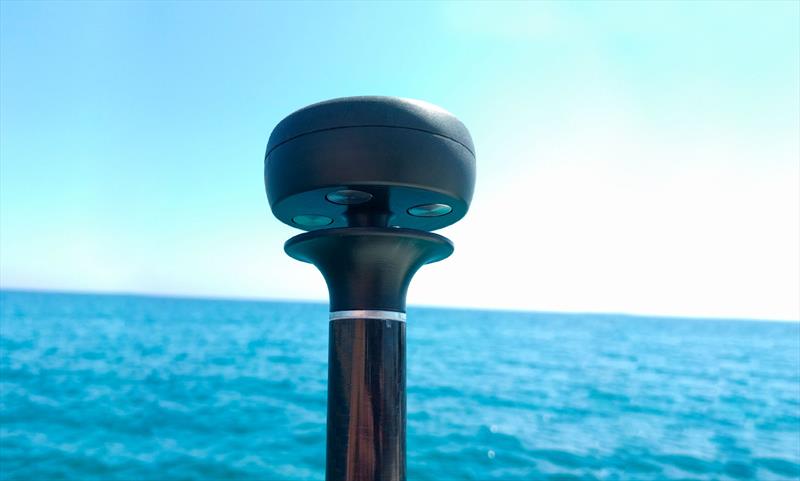
What is Marine Anemometer?
A marine anemometer is a specialized wind measuring instrument primarily used in marine navigation and meteorology. Designed to withstand harsh marine environmental conditions, these wind sensors provide accurate and reliable wind speed and directional data, essential for safe and efficient marine voyages.Specific Use of a Marine Anemometer
A marine anemometer, sometimes also referred to as a wind vane, utilizes various technologies such as wind cups, vanes, or ultrasonic signals to measure wind speed and direction. The data derived from the marine anemometer allows sailors to make accurate navigational decisions and ensures the safety of the vessel and its crew during the journey.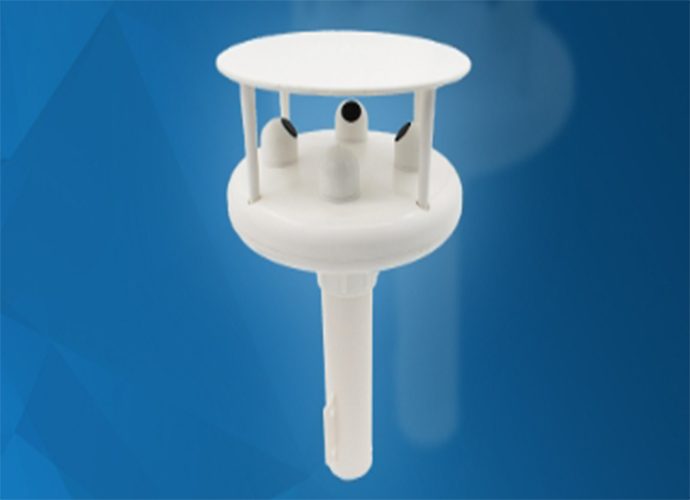
Importance of Marine Anemometer in Maritime Navigation
Role of a Marine Anemometer in Navigational Safety
The anemometer marine plays a pivotal role in the safe navigation of vessels. By providing real-time data on wind speeds and directions, it helps sailors make crucial decisions on sail trim, course plotting, and vessel speed. Without a reliable marine anemometer, sailors would find it challenging to navigate safely, especially in turbulent weather conditions and rough seas.Operational Decision-Making with a Marine Anemometer
In addition to improving safety, the marine anemometer is equally essential for operational efficiency. Wind information is crucial in optimizing fuel consumption, maintaining course, and ensuring timely arrivals. These factors can significantly impact the operational costs and overall efficiency of marine logistics. By expanding our understanding of marine anemometers, we can better appreciate their critical role in maritime operations, underpinning efficient and safe navigational practices.Three Types of Marine Anemometer
| Anemometer Type | How It Works | Key Features or Models | Pros and Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonic Marine Anemometer | Utilizes ultrasonic pulses to measure wind speed, with the time taken by these pulses indicating wind velocity. | Notable model: R.M. Young Anemometer, which is durable and accurate in harsh marine conditions. | Pros: High accuracy, quick response, low maintenance Cons: Higher cost, additional power supply required |
| Heated Marine Anemometer | Measures wind speed by the cooling effect of the wind on a heated element, with more wind leading to more cooling. | Optimized for use in low airflow conditions and in confronting extreme weather like icing. | Pros: Effective in low airflow and extreme weather conditions Cons: Sensitive to temperature changes, more maintenance |
| Mobile Marine Anemometer | Portable and measures wind using traditional cup or vane mechanisms. | Features beneficial for individual sailors, such as ease of installation and wireless capability. | Pros: Portable, user-friendly, real-time data Cons: Might not be as accurate as larger, fixed anemometers |

Marine Anemometer for Sale: A Detailed Analysis
When it comes to understanding the intricacies involved in the pricing of marine anemometers, several aspects come into play that contribute to the final cost.What Factors Affect the Price of a Marine Anemometer?
Quality and Precision- Significance: The accuracy and reliability of a marine anemometer play a pivotal role in its pricing. Higher precision often dictates a higher price.
- Reasoning: Accurate measurements are crucial for navigational safety and operational efficiency in the marine environment, thus justifying the investment.
- Influence on Price: Features such as wireless data transmission, digital displays, and data logging functionality can substantially increase the price.
- Benefit: These features offer enhanced usability and data management, making them valuable for intensive marine applications.
Durability
- Material and Design Costs: Marine anemometers designed to withstand extreme weather, such as saltwater corrosion and high winds, often use premium materials, contributing to a higher cost.
- Longevity: Durable designs ensure long-term serviceability, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Brand Value: Established brands with a track record of reliability and customer satisfaction can command higher prices for their marine anemometers.
- Warranty and Support: Part of the price can be attributed to the comprehensive after-sales support and warranty services offered by reputable brands.
Marine Anemometer Installation Tips and Maintenance Guidelines
Smooth and precise functioning of a anemometer marine is largely dependent on its correct installation and subsequent maintenance. Optimal installation helps ensure accurate readings, while regular maintenance supports device longevity. This guide will outline key tips to help you get the best performance out of your marine anemometer.Best Practices for Installing a Marine Anemometer Onboard
Site SelectionWhen installing a marine anemometer, it is crucial to select an appropriate site where wind flow is least obstructed. Choosing a high point away from superstructures will ensure the most accurate readings.
Alignment
Proper alignment with the vessel's bow is crucial. A misaligned anemometer can provide inaccurate wind direction readings.
Secure Installation
Ensure that the marine anemometer is securely installed, minimizing the potential for vibration or movement that could jeopardize the instrument's operation or reading accuracy.
Accessibility
Install the anemometer in a location that is easily accessible for cleaning, maintenance, and battery replacement (if applicable).
Ensuring Accurate Readings and Longevity: Maintenance Tips for Marine Anemometers
Regular CleaningThe marine anemometer should be cleaned regularly to remove accumulated salt, dirt, and debris that might impede its operation. Strictly follow manufacturer's guidelines concerning cleaning agents and methods.
Routine Inspections
Regularly inspect the marine anemometer for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Early detection will allow for timely replacement of parts, ensuring the device's functionality and longevity.
Calibration
Check the marine anemometer's calibration regularly. Calibration drift, though uncommon, can occur, especially after harsh weather conditions.
Proper Winterization
In cold regions where icing may occur, proper winterization of the marine anemometer is important. This might include removing the device during the off-season or protecting it with a specific cover.
Correct installation and diligent maintenance greatly enhance the service life and accuracy of a marine anemometer. Therefore, understanding and practicing the right techniques can result in reliable, long-term performance of this crucial marine device.
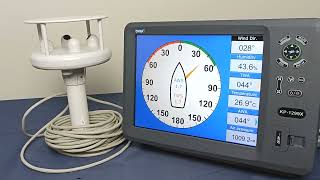
Choosing the Right Marine Anemometer
Selecting the right marine anemometer is a crucial step for mariners, shipowners, and maritime operations. The efficiency of marine navigation significantly hinges on the ability to accurately measure wind speed and direction.Importance of Choosing the Right Marine Anemometer
The choice of a marine anemometer can drastically affect the operational efficiency and safety of marine vessels. Accurate wind data is vital for making informed decisions regarding course adjustments, sail settings, and fuel management. Moreover, for certain maritime activities such as cargo loading and fishing operations, selecting the appropriate marine anemometer can lead to significant improvements in safety and productivity.
The Impact of Accurate Wind Readings in Marine Navigation
The Role in SafetyAccurate wind readings play a critical part in ensuring the safety of the vessel and crew. They assist in navigating through harsh weather conditions and avoiding potential hazards that can arise from sudden wind changes.
Efficiency and Fuel Management
Precise wind data allows for optimal routing and sail setting, significantly enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing operational costs. Accurate wind measurements mean fewer corrections and adjustments, leading to smoother and faster voyages.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Your Marine Anemometer
AccuracyThe primary consideration should be the anemometer's accuracy. For marine operations, even slight inaccuracies can lead to miscalculations, affecting navigation and safety.
Durability
Given the harsh marine environment, the chosen marine anemometer should be highly durable, resistant to saltwater corrosion, and capable of performing in extreme conditions.
Range
It's essential to select a marine anemometer with a wide measuring range, ensuring it can accurately capture both low winds for precise maneuvering and high winds during stormy conditions.
Popular Marine Anemometer Models in the Market
While there are numerous models available, each with its own set of features, some have gained popularity for their reliability and performance:Ultrasonic Marine Anemometers
Known for their precision and durability, ultrasonic models are becoming the go-to choice for professionals seeking high-quality wind data.
Cup Anemometers
These are widely used due to their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. They are particularly favored in less demanding applications.
Choosing the right marine anemometer involves careful consideration of many factors, including accuracy, durability, and range. By understanding the importance of accurate wind readings and evaluating the available options, mariners can select a device that ensures safety, efficiency, and operational excellence on the high seas.
Key Marine Anemometer Features
- Accurate wind speed and direction reading
- Robust and waterproof build
- Easy installation
- High visibility digital displays
- Durable under severe weather conditions

>>Click here view more




















